American marten (Martes americana) COSEWIC assessment and status report: chapter 5
Distribution
Global and Canadian range
The American marten is distributed throughout the coniferous forests of the boreal and taiga zones of North America (Gibilisco 1994). While habitat loss and fragmentation due largely to logging have resulted in population declines and extirpations in many regions (Bissonette et al. 1989, Thompson 1991), conservation efforts and forest succession have allowed some populations to re-establish (Gibilisco 1994). The Canadian range of M. americana atrata includes Newfoundland, northern Quebec and Labrador. The genetically distinct Newfoundland population occurs only on the island of Newfoundland.
Newfoundland range
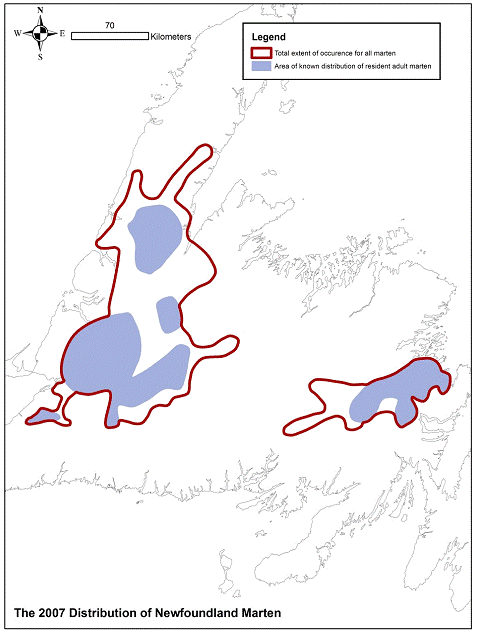
The historical range of American marten in Newfoundland is assumed to have been contiguous within forested areas (Bergerud 1969). The range contracted in the 20th century, in all likelihood as a result of overtrapping and the removal of forest habitat by logging and fires. Sequential marten publications and status reports by Bergerud (1969), Skinner (1979), Snyder (1985), Lemon (1996) and COSEWIC (2000) documented a trend in range reduction. The current extent of occurrence is 68,700 km² (A. Filion, pers. comm., 2006), and includes a large unoccupied area between the eastern and western populations (Figures 2 and 3).
The current range includes 23,383 km² of pockets of forested habitats in western (Figure 2) and eastern Newfoundland (Figure 3). Four core areas occupied by adult resident marten are recognized in the Terra Nova, Main River and Little Grand Lake-Red Indian Lake and St. George’s areas (2,829 km², 2,177 km², and 6,232 km², 590 km², respectively, totalling 11,828 km²) (I. Schmelzer, pers. comm., 2007). Isolated adult residents and juveniles or unconfirmed residents occupy an additional 11,555 km² of peripheral areas (I. Schmelzer, pers. comm., 2007). This area includes a potential 5th core area of 260 km² in the Lobster House area.
Figure 2. Recent distribution of the American marten in western Newfoundland. Map created by Wildlife Division, Newfoundland & Labrador Department of Environment and Conservation.

Figure 3. Recent distribution of the American marten in Eastern Newfoundland. Map created by Wildlife Division, Newfoundland & Labrador Department of Environment and Conservation.

The current area of occupancy (23,383 km², with 11,828 km² in core areas, Figure 4) is greater than that estimated in 1985 (13,356 km², with 4,551 km² in core areas) (Hancock et al. 1985). There have been gains in distribution as transplanted populations in the Main River and Terra Nova areas have increased. The data base for marten distribution, based on live-trapping, accidental captures, radio telemetry, bait stations, and incidental sightings has improved in recent years, giving more accurate delineations of core and peripheral areas (I. Schmelzer, pers. comm., 2007). The area of occupancy is believed to be 25% of the historical distribution, or about 60% of the distribution observed in the mid-20th century (The Newfoundland Marten Recovery Team, in preparation, a).
Figure 4. The known total distribution of American marten on the island of Newfoundland in 2007.
Page details
- Date modified: